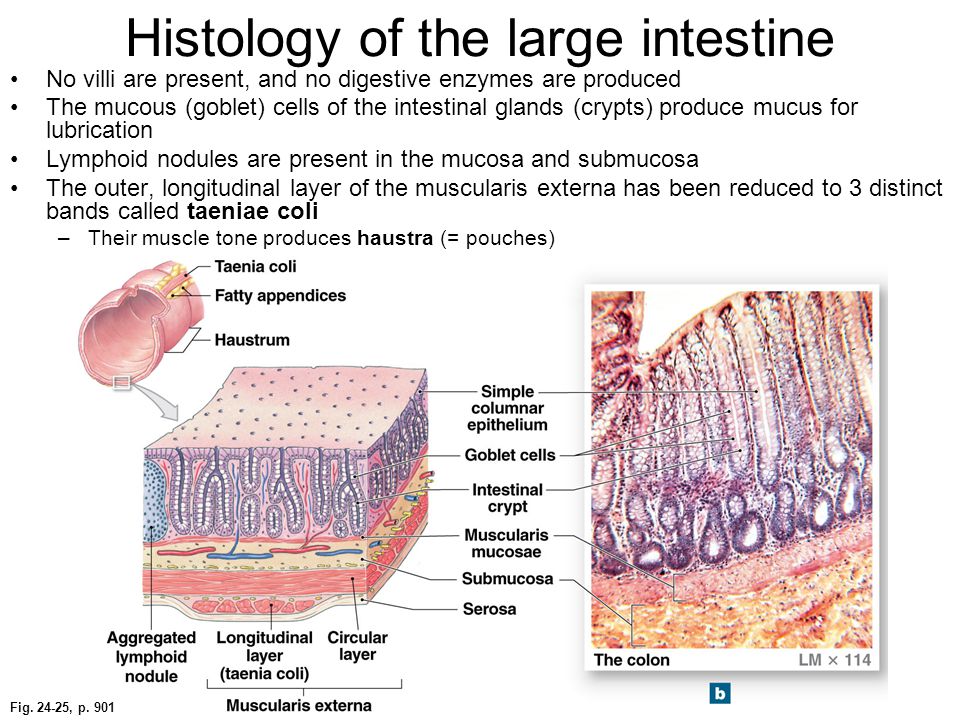
Lining Of Large Intestine Cells . learn about the structure and function of the large intestine, which has taeniae coli, intestinal glands, and goblet cells. — intestinal epithelial cells (iecs) provide a physical and biochemical barrier that segregates host tissue and. — intestinal epithelial cells greatly contribute to the maintenance of the symbiotic relationship between gut. Both the small intestine and the large intestine have goblet cells, but they are. the wall of the large intestine is lined with simple columnar epithelium. The web page also explains the crypts. — the intestine is the most highly regenerative organ in the human body, and it can replace its lining every five to seven days.
from medicienterprises.com
— intestinal epithelial cells (iecs) provide a physical and biochemical barrier that segregates host tissue and. the wall of the large intestine is lined with simple columnar epithelium. The web page also explains the crypts. — intestinal epithelial cells greatly contribute to the maintenance of the symbiotic relationship between gut. Both the small intestine and the large intestine have goblet cells, but they are. learn about the structure and function of the large intestine, which has taeniae coli, intestinal glands, and goblet cells. — the intestine is the most highly regenerative organ in the human body, and it can replace its lining every five to seven days.
Great Bowel Movements Laws Governing the Ecosystem of Large Intestine
Lining Of Large Intestine Cells — the intestine is the most highly regenerative organ in the human body, and it can replace its lining every five to seven days. — the intestine is the most highly regenerative organ in the human body, and it can replace its lining every five to seven days. the wall of the large intestine is lined with simple columnar epithelium. — intestinal epithelial cells greatly contribute to the maintenance of the symbiotic relationship between gut. The web page also explains the crypts. Both the small intestine and the large intestine have goblet cells, but they are. learn about the structure and function of the large intestine, which has taeniae coli, intestinal glands, and goblet cells. — intestinal epithelial cells (iecs) provide a physical and biochemical barrier that segregates host tissue and.
From www.cell.com
Primary CellDerived Intestinal Models Recapitulating Physiology Lining Of Large Intestine Cells — the intestine is the most highly regenerative organ in the human body, and it can replace its lining every five to seven days. — intestinal epithelial cells greatly contribute to the maintenance of the symbiotic relationship between gut. — intestinal epithelial cells (iecs) provide a physical and biochemical barrier that segregates host tissue and. the. Lining Of Large Intestine Cells.
From doctorlib.info
Overview of Gastrointestinal Function & Regulation Ganong’s Review of Lining Of Large Intestine Cells — the intestine is the most highly regenerative organ in the human body, and it can replace its lining every five to seven days. — intestinal epithelial cells (iecs) provide a physical and biochemical barrier that segregates host tissue and. The web page also explains the crypts. the wall of the large intestine is lined with simple. Lining Of Large Intestine Cells.
From mavink.com
The Small Intestine Diagram Lining Of Large Intestine Cells The web page also explains the crypts. — the intestine is the most highly regenerative organ in the human body, and it can replace its lining every five to seven days. — intestinal epithelial cells greatly contribute to the maintenance of the symbiotic relationship between gut. Both the small intestine and the large intestine have goblet cells, but. Lining Of Large Intestine Cells.
From stock.adobe.com
Small intestine lining anatomy, a fold of the intestinal lining, villi Lining Of Large Intestine Cells The web page also explains the crypts. — the intestine is the most highly regenerative organ in the human body, and it can replace its lining every five to seven days. — intestinal epithelial cells greatly contribute to the maintenance of the symbiotic relationship between gut. — intestinal epithelial cells (iecs) provide a physical and biochemical barrier. Lining Of Large Intestine Cells.
From courses.lumenlearning.com
The Small and Large Intestines Anatomy and Physiology II Lining Of Large Intestine Cells The web page also explains the crypts. — the intestine is the most highly regenerative organ in the human body, and it can replace its lining every five to seven days. — intestinal epithelial cells greatly contribute to the maintenance of the symbiotic relationship between gut. Both the small intestine and the large intestine have goblet cells, but. Lining Of Large Intestine Cells.
From mavink.com
Large Intestine Cells Lining Of Large Intestine Cells learn about the structure and function of the large intestine, which has taeniae coli, intestinal glands, and goblet cells. — the intestine is the most highly regenerative organ in the human body, and it can replace its lining every five to seven days. The web page also explains the crypts. the wall of the large intestine is. Lining Of Large Intestine Cells.
From spyrogenes.deviantart.com
Small Intestine (COLUMNAR EPITHELIUM) LPO MAG by Spyrogenes on DeviantArt Lining Of Large Intestine Cells The web page also explains the crypts. — the intestine is the most highly regenerative organ in the human body, and it can replace its lining every five to seven days. — intestinal epithelial cells greatly contribute to the maintenance of the symbiotic relationship between gut. — intestinal epithelial cells (iecs) provide a physical and biochemical barrier. Lining Of Large Intestine Cells.
From courses.lumenlearning.com
Mucosal Surfaces and Immune Tolerance Biology for Majors II Lining Of Large Intestine Cells The web page also explains the crypts. — the intestine is the most highly regenerative organ in the human body, and it can replace its lining every five to seven days. the wall of the large intestine is lined with simple columnar epithelium. learn about the structure and function of the large intestine, which has taeniae coli,. Lining Of Large Intestine Cells.
From www.alamy.com
Intestine lining and villi , Food digestion and absorption Stock Photo Lining Of Large Intestine Cells — the intestine is the most highly regenerative organ in the human body, and it can replace its lining every five to seven days. the wall of the large intestine is lined with simple columnar epithelium. — intestinal epithelial cells greatly contribute to the maintenance of the symbiotic relationship between gut. Both the small intestine and the. Lining Of Large Intestine Cells.
From ahmadkruwhickman.blogspot.com
Which Cells in the Small Intestine's Mucosa Secrete Mucus Lining Of Large Intestine Cells — intestinal epithelial cells (iecs) provide a physical and biochemical barrier that segregates host tissue and. — intestinal epithelial cells greatly contribute to the maintenance of the symbiotic relationship between gut. — the intestine is the most highly regenerative organ in the human body, and it can replace its lining every five to seven days. The web. Lining Of Large Intestine Cells.
From journals.physiology.org
Intestinal epithelial regeneration active versus reserve stem cells Lining Of Large Intestine Cells — the intestine is the most highly regenerative organ in the human body, and it can replace its lining every five to seven days. the wall of the large intestine is lined with simple columnar epithelium. — intestinal epithelial cells (iecs) provide a physical and biochemical barrier that segregates host tissue and. — intestinal epithelial cells. Lining Of Large Intestine Cells.
From www.pinterest.jp
small intestine histology labeled Google Search Anatomy and Lining Of Large Intestine Cells learn about the structure and function of the large intestine, which has taeniae coli, intestinal glands, and goblet cells. Both the small intestine and the large intestine have goblet cells, but they are. — intestinal epithelial cells greatly contribute to the maintenance of the symbiotic relationship between gut. The web page also explains the crypts. the wall. Lining Of Large Intestine Cells.
From dr-wendihealth.com
How can you tell if your small intestine is healthy or damaged? Dr Lining Of Large Intestine Cells — intestinal epithelial cells greatly contribute to the maintenance of the symbiotic relationship between gut. The web page also explains the crypts. — intestinal epithelial cells (iecs) provide a physical and biochemical barrier that segregates host tissue and. — the intestine is the most highly regenerative organ in the human body, and it can replace its lining. Lining Of Large Intestine Cells.
From courses.lumenlearning.com
Bacterial Infections of the Gastrointestinal Tract Microbiology Lining Of Large Intestine Cells the wall of the large intestine is lined with simple columnar epithelium. learn about the structure and function of the large intestine, which has taeniae coli, intestinal glands, and goblet cells. The web page also explains the crypts. — the intestine is the most highly regenerative organ in the human body, and it can replace its lining. Lining Of Large Intestine Cells.
From courses.lumenlearning.com
The Immune Response against Pathogens Anatomy and Physiology II Lining Of Large Intestine Cells Both the small intestine and the large intestine have goblet cells, but they are. The web page also explains the crypts. learn about the structure and function of the large intestine, which has taeniae coli, intestinal glands, and goblet cells. — intestinal epithelial cells greatly contribute to the maintenance of the symbiotic relationship between gut. the wall. Lining Of Large Intestine Cells.
From www.jobilize.com
Stratified epithelium, Epithelial tissue, By OpenStax (Page 4/37 Lining Of Large Intestine Cells The web page also explains the crypts. learn about the structure and function of the large intestine, which has taeniae coli, intestinal glands, and goblet cells. Both the small intestine and the large intestine have goblet cells, but they are. — intestinal epithelial cells (iecs) provide a physical and biochemical barrier that segregates host tissue and. —. Lining Of Large Intestine Cells.
From courses.lumenlearning.com
The Small and Large Intestines Anatomy and Physiology II Lining Of Large Intestine Cells — intestinal epithelial cells (iecs) provide a physical and biochemical barrier that segregates host tissue and. — intestinal epithelial cells greatly contribute to the maintenance of the symbiotic relationship between gut. the wall of the large intestine is lined with simple columnar epithelium. Both the small intestine and the large intestine have goblet cells, but they are.. Lining Of Large Intestine Cells.
From aehidroterapiadecolon.com
The Very Intelligent Intestine Epithelial Cell Asociación Española de Lining Of Large Intestine Cells the wall of the large intestine is lined with simple columnar epithelium. The web page also explains the crypts. — intestinal epithelial cells (iecs) provide a physical and biochemical barrier that segregates host tissue and. — intestinal epithelial cells greatly contribute to the maintenance of the symbiotic relationship between gut. — the intestine is the most. Lining Of Large Intestine Cells.